Native microbial communities (microbiomes) of the vertebrate gut exert vital effects on host ecology, physiology, and evolution. This project explores the potential that the gut microbiome of herbivorous fish plays a vital role in biochemically degrading algal toxins consumed by the host fish, and therefore structuring diet choice and ecology. The student will work jointly between the labs of Drs. Mark Hay and Frank Stewart to test this broad hypothesis, likely focusing on the microbiomes of specific coral reef herbivores.
The characterization of sediment biogeochemistry at high spatial and temporal resolution is a necessary step in predicting the overall pathways and extent of hydrocarbon degradation in areas affected during and after an oil spill. However, geochemical data for sediments from deeper environments are scarce, and most studies do not measure the full suite of terminal electron acceptors involved in sediment diagenesis.
Plastic marine debris or the plastisphere impacts marine organisms through ingestion, entanglement, and as a source of toxic chemicals. The plastisphere could also have a major impact on biogeochemical cycles in the oceans. Plastics are transported via major ocean currents to central gyres, where they reside for decadal time scales. The amount of plastic waste is large, exceeding 2 kg/ km2 in central gyres. Even the most recent ocean surveys cannot account for the amount of debris estimated to enter the ocean, with inputs and outputs differing by orders of magnitude.
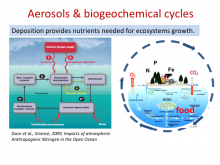
The sustainability of human civilization and its evolving lifestyle depends fundamentally on a sustainable food and energy supply. This can largely be linked to the availability of reactive nitrogen (Nr), phosphorus (P) and trace-element nutrient availability for natural and managed ecosystems. Nr, P and Fe are known to stimulate productivity while other elements, like Cu and Mn, can be toxic for ecosystems. Nr is also a critical link for the carbon cycle, and directly/indirectly impacts climate and human/ecosystem health.